If Windows 10 or an app isn't behaving as expected, you can use the Event Viewer to understand and troubleshoot the issue, and in this guide, we'll show you how.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.

On Windows 10, the Event Viewer is a handy legacy tool designed to aggregate event logs from apps and system components into an easily digestible structure, which you can then analyze to troubleshoot and fix software or hardware problems with your computer.
Typically, most users don't use or know about the Event Viewer. However, it should be the first place to check to troubleshoot problems since virtually every hardware failure, app crash, driver malfunction, system issue, security access, and events from apps and services working without issues, will be recorded in this database.
If your device is suddenly rebooting without reason, freezing up, drivers aren't behaving as expected, or you're experiencing Blue Screen of Death (BSoD), the Event Viewer on Windows 10 may contain logs with the information you need to resolve the problem or at least find out clues to help you find a solution.
In this Windows 10 guide, we'll walk you through the steps to navigate and use the Event Viewer on your device.
On Windows 10, the Event Viewer exists to help you monitor apps and system components as well as troubleshoot problems.
To open the Event Viewer on Windows 10, simply open start and perform a search for Event Viewer, and click the top result to launch the console.
The experience is divided into four main groups, including "Custom Views," "Windows Logs," "Applications and Services Logs," and "Subscriptions," and each group stores related logs.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.
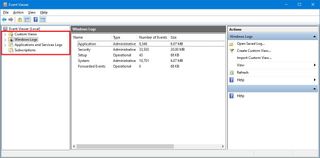
Although each group can hold different app and system logs, most of the time, you'll only be analyzing the Application, Security, and System logs inside the "Windows Logs" group to investigate an issue.
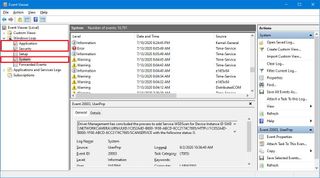
Inside "Application," you'll find events about the interface and other essential components to run an app. In the "Security" category that's where the logs events related to login attempts and security features are grouped, and the "System" category records the logs related to apps installed on Windows 10.
The Event Viewer can track three kinds of event levels, including Error, Warning, and Information. The "Error" logs, as the name implies, indicate problems that require immediate attention. The "Warning" logs are not necessarily significant. However, they might signal that something is not working as expected, and the "Information" logs are simply events that record normal operation of apps and services.
Usually, all apps should log events in this database, but it's not always true for many third-party applications.
If the device is working normally, you will still see errors and warnings, but they'd likely not be anything concerning. For example, sometimes, you may see an error if a service couldn't load at startup, but it restarted at a later time normally. The time service couldn't synchronize correctly, Windows 10 couldn't access a file on a network shared folder because there was a connection problem — or an app suddenly crashed, but then you opened it again, and it continued to work without issues.
While in the console, you can select one of the main groups to view additional information, such as the number of events and size on disk for each view. Or you can select "Event Viewer" from the top-left to get an overview and summary events, recently view notes, and log summary.
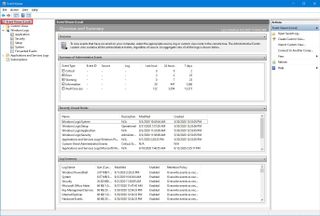
If you select one of the groups, on the right side, you'll see all the events with their "Level" information, "Date and Time" of creation, "Source," and "Event ID," and "Task Category." If you want to see more details, you can select the event, and the information will be displayed at the bottom of the console, or you can double-click the event to access more details.
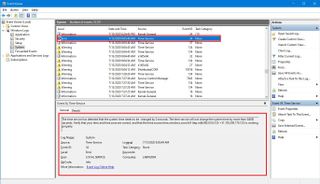
In the event properties window, the "General" tab includes an easy-to-understand description of the error, warning, or information.
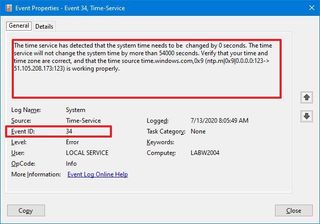
Usually, the description should give you enough information to understand and resolve the issue. However, the "Event ID" is also an important piece of information, as you can use it to search online to find out more information, and possible instructions to fix the problem.
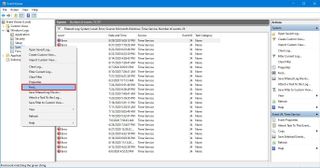
If you're looking for a specific event, the console provides at least two ways to find events using the filters or keyword search.
Advanced search
To use the filters to find a specific type of log, use these steps:
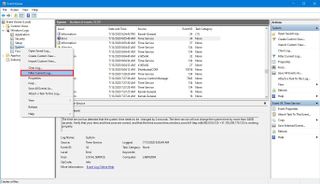
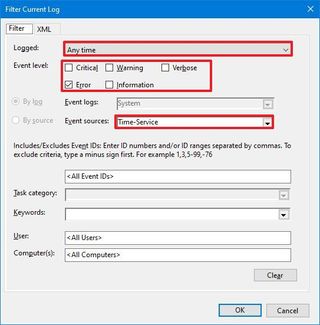
Once you complete the steps, related logs will appear filtered in the console. If you want to clear the current filter, right-click the group, and select the Clear Filter option.
Basic search
To use a keyword to find an error, warning, or information event with Event Viewer, use these steps:
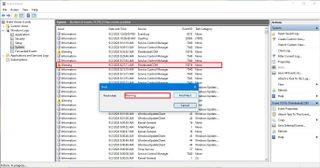
After you complete the steps, the event will be highlighted in the list if a match is found.
In the case that you frequently search for the same type of events, the Event Viewer also comes with an option to create custom views to quickly filter the logs to view only those that are relevant to you.
To create a custom view in the Event Viewer, use these steps:
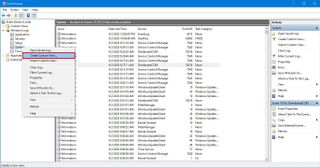
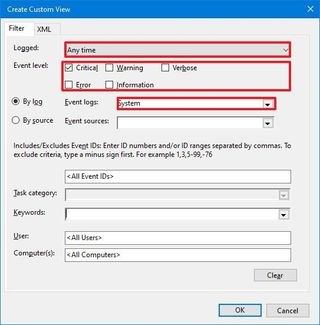 Event Viewer create custom view" width="" />
Event Viewer create custom view" width="" />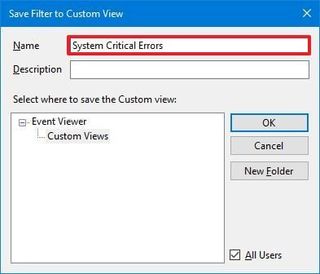
Once you complete the steps, the next time you need to view specific logs, you can expand the "Custom Views" folder and select the view you created.
On Windows 10, logs help you track your device's health and troubleshoot problems, and you should keep them as long as possible. However, you can clear the log history to free up space or make it easier to track an existing problem.
To clear the log history of a particular category, use these steps:
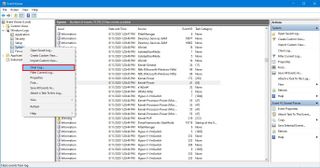
After you complete the steps, the events will be deleted, and the console will start recording new events.
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.